What is MES software? Structure, functions & advantages
Reading time: 6 min
In modern manufacturing, hardly any company can avoid the term MES Software over. Production planning is becoming increasingly complex, customer requirements more individual - traditional ERP systems are quickly reaching their limits.

Automated production line with networked processing cells, controlled by MES software
The role of MES software in today's industry should not be underestimated. Companies are faced with the challenge of optimizing their production processes and at the same time reacting flexibly to constantly changing market requirements. It offers a powerful solution by providing real-time data from production, creating transparency and facilitating control. This enables companies not only to increase their efficiency, but also to sustainably improve the quality of their products.
Another advantage lies in the intelligent use of production data. Modern systems make it possible to identify trends at an early stage in order to manage resources in a targeted manner. Companies benefit from reduced production costs and optimized processes.
Adaptability remains one of the biggest challenges in modern manufacturing. Companies must make their production processes agile in order to meet the growing expectations of their customers. MES software plays a crucial role in this by improving planning, control and communication between systems and departments.
However, implementation requires more than just technology: employees need to be trained and involved in the change. Companies that take this step often report increased acceptance and higher productivity overall.
But what exactly is behind a Manufacturing Execution System (MES)? What functions does it offer, how is it structured and what are the advantages for manufacturing companies?
In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about MES software: From the basic definition to central requirements, typical modules and areas of application - right through to the question of why modern solutions such as our MCS are often superior to classic MES.
What is MES software?
MES stands for Manufacturing Execution Systemproduction control system. It closes the gap between ERP and production by controlling, monitoring and documenting production processes in real time.
The adaptability of MES software is a decisive advantage. Companies from a wide range of industries can benefit from modular structures and use customized solutions - from mechanical engineering to the food industry.
Definition & basics
One example of the use of MES software is the automotive industry, where numerous components have to be precisely coordinated and assembled. An MES makes it possible to call up the production status in real time, detect deviations immediately and react in a targeted manner.
The modules of MES software can be used both independently and integrated. This enables seamless communication between all areas - from order acceptance to delivery. Companies shorten their throughput times, increase customer satisfaction and improve their competitiveness.
MES systems are used in a wide variety of production environments, including:
- Series production
- Variant production
- Process industry
- Medium-sized suppliers
Requirements for an MES
A powerful MES forms the backbone of modern production. In order to make production processes efficient, flexible and future-proof, it must meet a wide range of requirements - technical, structural and organizational.
1. flexible integration capability
An MES must integrate seamlessly into existing system landscapes. This includes
- Connection to machine control systems (PLC, CNC, robots)
- Support for modern interfaces such as OPC UA, MQTT, REST API
- Integration with ERP, SCADA, CAQ and PLM systems
2. real-time capability and transparency
Real-time data is the key to efficient control. A modern MES offers:
- Live monitoring of production
- Traceability on a component, batch or order basis
- OEE analysis & performance monitoring
- Energy consumption and predictive maintenance evaluations

Live data in the MCS: machine and order status at a glance
3. automation support
An MES must not slow down automation, but actively enable it:
- Intelligent order distribution according to priorities, availability and rules
- Support for lights-out manufacturing and unmanned shifts
- Connection of autonomous systems such as AGVs and robot cells
- Use of AI for decision support and process optimization
4.modularity & scalability
Production processes change - an MES must be able to grow with them:
- Scalable architecture for companies of any size
- License and function models in line with company development
- From manually assisted production steps to fully automated production
Additional requirements for fully automated production
In highly automated production environments, the requirements that a future-proof MES must fulfill are even stricter:
- Self-optimizing control loops: Dynamically adapt processes based on real-time data
- Zero-touch workflows: Fully automated processes without human intervention
- Process safety & validation: Highest requirements for data integrity, availability and traceability
- Visualization & Simulation: Use of digital twins, material flow simulations and production forecasts
An MES such as our MCS fulfills precisely these requirements - from the manual line to fully autonomous production.
Typical modules of MES software
An MES usually consists of the following core modules:
- Order managementManage production orders and distribute them to machines and employees
- Machine connection & data acquisitionRecord status and production data in real time
- Production data acquisition (PDA)Feedback from employees on orders, shifts and disruptions
- Key performance indicators & OEECalculation of key figures up to Overall Equipment Effectiveness
- Quality managementMonitoring and documentation of quality data
- Shift & personnel schedulingEfficient use of resources
These modules are interlinked and provide a holistic overview of the entire production process.
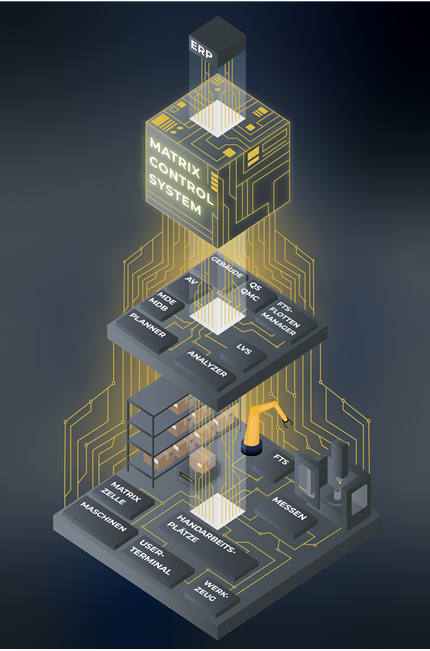
Functional architecture of the MCS - from the ERP level to the store floor
Advantages of MES software
The use of MES software offers a number of advantages:
- More transparency: Up-to-date insight into the production status at all times
- Less downtime: Faster reactions to faults
- Better planning capability: Informed decisions thanks to real-time data
- Increasing efficiency: Recognizing and exploiting potential
- Improved verification managementDocumentation for quality assurance and audits
- FlexibilityRapid adaptation to changing market conditions
Especially in dynamic markets, it is crucial to be able to react flexibly to new requirements - MES software provides the necessary basis for this.
Why MCS? - Advantages of our system
While classic MES systems are often complicated, expensive and cumbersome, our MCS (Matrix Control System) a practice-oriented alternative:
- Simple operation - even for non-IT experts
- Modular and individually configurable
- Also ideal for medium-sized companies without unnecessary overheads
- Quick to implement and future-proof
The MCS was specially developed to meet the requirements of modern manufacturing companies and impresses with its user-friendliness and flexibility.

Conclusion: MES software as the key to digital production
In a dynamic market environment, it is crucial to be able to react flexibly to changing requirements - MES software provides the necessary basis for this. It functions not only as a technical tool, but also as a strategic success factor in the digital transformation, optimizing processes, increasing efficiency and enabling companies to hold their own in a highly competitive market. Our MCS (Matrix Control System) offers a practical alternative to traditional, complicated and costly MES systems. Specially developed for modern manufacturing companies, it impresses with its user-friendliness and flexibility. With our MCS, you get an adaptable, user-friendly solution that lays the foundation for sustainable success.